Sunday, December 5, 2010
Question for class on Wednesday (12/8)
While there were major racial issues in the US during the 1960's. Was or has there ever been racial issues in Germany. Other than during World War II.
RAF!!
- the causes
According to the author of the Der Baader Meinhof Komplex, the leaders of the new Germany, The Third Reich, were the same people in charge during Nazism. It was seen that anything that was going wrong in Germany was blamed on the Nazis or SS, like police brutality. The participants in RAF were sick of this, they wanted a new Germany separate from the Nazi occupied one.
- the three generations of activists
Received financial aid from Stasi (the security and intelligence agency of East German). They provided new identities and places to stay.
- the end of the RAF
Last attack was in 1993, no one was killed but the explosions caused about 67 million dollars in damages! In 1998 a German secret service received an 8 page faxes paper stating that after about 28 years the RAF was disbanding and ending the 'project.'
- the similarities between current day's terro attacks and the RAF (similarities and differences)
Obviously with the aftermath of the world trade centers attack we can say that now terrorist attacks are on a larger level. A similarity is that the RAF was attacking to give change Germany, now-a-days terrorists are attacking to make a change in the world.
http://www.nytimes.com/2009/08/16/movies/16kapl.html?_r=2
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Red_Army_Faction
Image- http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/9/97/Fahndungsplakat_-_RAF.jpg/421px-Fahndungsplakat_-_RAF.jpg
Tuesday, November 30, 2010
Der Baader Meinhof Complex
This movie confused me. I'm not sure if I missed it in the subtitles or if it was never made obvious to me, but I didn't understand what they were protesting. The movie wasn't a total lost. I got to see how translating isn't exact. Once the character said, "Ja," the subtitles were, "right on," which from my German 101 Ja is yes. Just an observation, did it in no way ruin the movie. On the plus side I learned how to say shit in German, SCHEISSE, SCHEISSE, SCHEISSE!
I did think it was cool how they communicated secretly so the guards wouldn't know what they were planning on doing. I thought it was interesting how the columnist at the beginning of the movie wasn't associated with the protestors. The police even 'unarresting' her. It was also interesting how they used her as a gateway to the prisoned protestors. And being able to use her power to break them out of prison.
I did think it was cool how they communicated secretly so the guards wouldn't know what they were planning on doing. I thought it was interesting how the columnist at the beginning of the movie wasn't associated with the protestors. The police even 'unarresting' her. It was also interesting how they used her as a gateway to the prisoned protestors. And being able to use her power to break them out of prison.
Saturday, November 20, 2010
Wednesday, November 17, 2010
Wednesday, November 10, 2010
Why the EU will continue to be a pivotal organization for Germany in the 21st century
- 1. Having all these countries being part of the EU means they all was the Euro. This is a good thing; it makes it easier spend money not having to worry about getting those countries currency. It also makes for easier trading when one countries money isn't worth more then another.2. Germany, along with other countries in the EU, lets non-citizens live in their country free of charge (taxes). This is good because it increases their population; along with that they are getting money from these people stimulating their economy.3. The EU unites Germany with other EU countries, giving them good connection for everything from trade to military.4. The EU is big on protecting the environment. This is good for Germany along with others because it will keep the country clean for future generation after the 21st Century.5. Now Germany is selling more than buying, they are flourishing. I only see it getting better in the 21st Century. Being part of the EU allows Germany (along with other member) to have their personal marketplace. Meaning that they have connections with other members, which makes it easy for other countries to buy German goods. With more and more countries wanting to become part of the EU, which will most likely happen in the 21st Century. This will open more doors and trading and selling/buying options with them.6. One plus for the countries in the EU are that people that live in a different EU country than they work pay taxes in the country they work. This is good and bad, if you have someone paying taxes in Germany but live France than France isn't getting that extra money from taxes.7. I'm not saying this would ever happen but if it were to happen we would see more swift movement to stop it. If Germany were to ever have another incident like they did with Hitler the EU would be able to unite with member countries to stop it.8. Since World War one and two Germany has been looked down upon. Being part of the EU makes them look like they are trying to fix their past and make a better future in the 21st Century.9. Being part of the EU, German citizens don't have to fear any unexpected economic wars or unexpected taxes on items. This allows them to sell product at whatever price they think they can get for it.10. EU allows Germany to remain a global competitor with the rest of the world.11. If Germany happens to become a poorer country in the 21st Century the EU will be there to help them. Mostly through other countries.12. The EU has decide in 2007 that 20% of the Union's power needs to come from renewable energy resources in the future. This, along with number 4, will help to ensure a good environment for the future generations.Work CitedClass Lecture
http://www.bundesregierung.de/nn_177700/Content/EN/Artikel/Europa-Uebersetzungen/07-02-13-2007-01-04-fuenfzig-jahre-eu-zehn-vorteile-fuer-deutschland/2007-01-04-fuenfzig-jahre-eu-zehn-vorteile-fuer-deutschland__en.html
Wednesday, November 3, 2010
Wednesday, October 27, 2010
Wednesday, October 20, 2010
Roles of Men and Women in the 20th Century
Matt
Kevin A.
Lexi
Lacey
Kayla
Danielle
Shelby
Andrew
The Military
Auxiliary Units
Served in the auxiliary units in the navy (Kriegshelferinnen), air force (Luftnachrichtenhelferinnen) and army (Nachrichtenhelferin)
Hundreds of women auxiliaries served for the SS in the concentration camp
Mata Hari
Dutch exotic dancer and prostitute
Accused of being a double agent for France and Germany during WWI
Was offered cash from a German consul for information the next time she visited France. Hari passed on old, outdated information to the German officer. Arrested in France and executed the same year by firing squad.
World War II
Germany’s men that weren’t in war were afraid to intervene when Russians were raping German women for the fear of being shot.
The women of Berlin braved the artillery fire to forage for food and water in the streets. It was they who fed the family, cleaned what mess they could, looked after the sick, hid their young girls and took the brunt of Russian brutality. Some women in Berlin were now looking down on their men as the weaker sex and felt disappointed in them and even sorry for them.
Women
· “For centuries, a woman's role in German society was summed up and circumscribed by the three "K" words: Kinder (children), Kirche (church), and Küche (kitchen)” (4)
· During the first world war women helped by entering into industrial style jobs while the men were off fighting in the war (1)
o Approximately 700,000 had begun working by the end of the war
o After WWI women won the right to vote (1919)
o Some women kept their jobs after the male soldiers returned
· During the Third Reich, women were meant to bear “Aryan” children and were taught to do so through aggressive propaganda. During WWII, Adolf Hitler wanted women to focus on the three Ks mentioned earlier and to not take place in war. (3)
· In 1975, German women were sought out to join the military (2)
Men
· All men age 18-23 have to attend a nine month training before going into war (2)
· There are approximately 200,000 soldiers that are considered professional and 300,000 that are more civilian, but are on reserve and are able to become active at any given time
· Many men were forced into war often through guilt and shame of their family and friends during the first two world wars
· All major German military and political leaders in the 20th century were men
Politics
1919 - women recieved the right to vote
Nazi Germany - Hitler wanted women to just have children to grow Germany's population. It was thier duty to ensure the future of the German race. Women were even given medals for having large families
1949 - Basic law declared men and women equal
1977 - Women gained rights to equal marriage
1980 - National office for women affairs set up in west germany to help work towards women quality
1988 - East germany, women made up almost 1/3 of Socialist unity party of germany (SED) while in west germany, women only made up abour 4.5% of the political party members.
1990 - Sabine Bergmann-Pohl was the president of the people's chamber of the GDR from april to october before the GDR ended
Domestic Life
Roles
In 1919 women received the right to vote
During World War II women took on some of the traditional jobs that the men left behind when they were fighting.
When the World War II was over women tended the wounded, buried the dead, salvaged belongings, and began rebuilding war-torn Germany by clearing away the rubble
In 1977 women got equal rights in marriage.
In West Germany
In the early 1980s women qualified for admission to universities in the same numbers as men.
The Basic Law of 1949 declared that men and women were equal.
But it was not until 1957 that the civil code was amended.
· After World War II women became homemakers and mothers again and largely withdrew from employment outside the home.
In East Germany
· Mid 1960s women accounted for half of all secondary school graduates.
· By 1975-76 they were the majority (53%)
· In the east, however, women remained in the workforce.
· As early as 1950, marriage and family laws also had been rewritten to accommodate working mothers.
· Abortion was legalized and funded by the state in the first trimester of pregnancy.
· An extensive system of social supports, such as a highly developed day-care network for children, was also put in place to permit women to be both mothers and workers.
· East Germany had to rely on women because of its declining population; the situation was made more critical by the fact that most of those fleeing to West Germany were men.
· 90% of the women worked outside of the home.
Business
Business in the German world is primarily made up of men. Women are not seen much in the business world. According to Wikipedia.com “Women are noticeably absent in the top tiers of German businesses. They only hold 9.2% of jobs in Germany's upper and middle management positions.” Although the Chancellor is a Woman it is still very difficult for woman to rise to management. There have been some issues in creating a law in Germany that would look at the quotas in companies so that woman have a chance to succeed. “ In 2001, the Justice Ministry established a governmental commission to develop a Corporate Governance Codex,.” quoted by Spiegel online. This is a document that was recently amended that could call on companies to increase the number of female managers. “Some companies in Germany such as Deutsche Telekom back in March and energy giant E., have recognized that incorporating more woman into their hierarchies is beneficial to their organization as a whole. Deutsche Telekom was the first DAX company to pledge to raise the percentage of women at mid to high level management to 30 percent.” Spiegel online. This does show us that there are some people who feel that woman can benefit their company, they are climbing the corporate ladder and there are ways that is making this happen either with the government help or by recognizing the good that both genders can play in a company. Stated by German information centre, “The business newspaper Handelsblatt was searching for tomorrow’s top women for Germany, the Financial Times Deutschland then proclaimed the “Age of Women”, and the magazine Capital even carried a cover story entitled “Der Chef trägt Prada” (The boss wears Prada)…. Nicola Leibinger-Kammüller has been managing the machine tool company Trumpf for a number of years now. Simone Bagel-Trah, a representative of the Henkel family, has been chair of the supervisory board of the Düsseldorf washing power and consumer goods company since last year and thus one of Germany’s most powerful women.” This just goes to show that woman can and are ready to make it to the top in the business world.
Simone Bagel-Trah
Education
During the early part of the twentieth century predominantly men went to school with intentions of going to university. By the mid-1960s women accounted for nearly half of all secondary school graduates with intentions on studying at institutes of higher learning in the GDR. Just fifteen years later they made up the majority with fifty-three percent. Supplementary payments and child care were provided to assist women in completing their studies. Women in west Germany did not qualify for admission into universities until the early 1980's. Therefore, west German women had more traditional familial relations, and did not have great ambitions for admission into particular academic departments, and for professional employment after graduation.
Sources
http://womenshistory.about.com/library/ency/blwh_germany_women.htm http://www.germanculture.com.ua/library/weekly/aa080601c.htm
Pictures
Tuesday, October 19, 2010
Men and Women's Role in the 20th Century in the Military
Women:
- Served in the auxiliary units in the navy (Kriegshelferinnen), air force (Luftnachrichtenhelferinnen) and army (Nachrichtenhelferin)
- Hundreds of women auxiliaries served for the SS in the concentration camps
- Also under ‘order’ to produce more pure Aryan children for future wars
Mata Hari:
- Dutch exotic dancer and prostitute
- Accused of being a double agent for France and Germany during WWI
- Was offered cash from a German consul for information the next time she visited France. Hari passed on old, outdated information to the German officer. Arrested in France and executed the same year by firing squad.
Women not in war in Germany:
- Germany’s men that weren’t in war were afraid to intervene when Russians were raping German women for the fear of being shot.
- The women of Berlin braved the artillery fire to forage for food and water in the streets. It was they who fed the family, cleaned what mess they could, looked after the sick, hid their young girls and took the brunt of Russian brutality. Some women in Berlin were now looking down on their men as the weaker sex and felt disappointed in them and even sorry for them.
Sunday, October 17, 2010
The best three class blogs in German 110 Fall 2010
Tuesday, October 5, 2010
Class Discussion
In class yesterday we talked about the events that made All Quiet on the Western Front such a famous book. Below are some points we discussed:
- The book is a tribute to the lost generation of people that were in the first World War.
- We talked about Himmelstoss and how his outside life without authority affected how we was during the war, power crazy.
- Germans either fight authority or suck up to authority
- How the war was the identity of the men who were in the war. When they went to war they didn't have an identity so the war became it. And after the war they no longer had an identity.
- How the book was advertised well and how it became such a popular book after the raw emotions and feelings of the war settled and past 10 years later.
- Erich Maria Remarque became filthy rich with the book.
- Anti-War book
- The characters in the book represented the whole generation
Tuesday, September 28, 2010
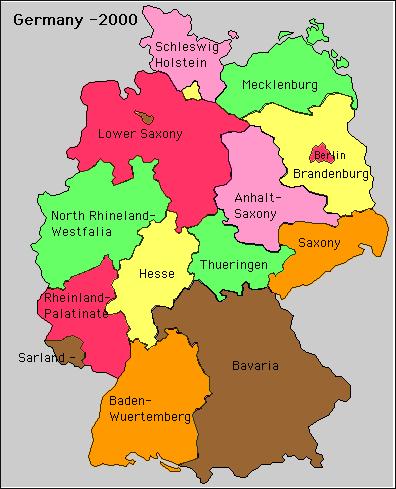
Lower Saxony/ Niedersachsen
Lower Saxony
Where is Lower Saxony located?
Located in the northwestern part of Germany
Lower Saxony borders many other German states:
- Southeast: Thuringia
- East: Brandenburg and Saxony-Anhalt
- North: Hamburg and Schleswig-Holstein
- South: Hesse
- Southwest: North Rhine- Westphalia
- Northeast: Mecklenburg-Vorpommern
How many live here?
- 7,977,000 people
- 4th largest state in population
- In population:
- Lower Saxony is equivalent to the population of Minnesota and Iowa together
- It is about half the size of Indiana
- Second largest state in size
- 20% of the state is designated to nature conservation
- Agriculture and farming make up a big part of the economy
- Automobile manufacturing and automobile parts manufacturing are also important economic part of Lower Saxony
- Volkwagon has 5 production plants here along with its headquarters, which is located in Wolfsburg
- The capital of Lower Saxony is Hannover.
- Hannover is also the largest city in Lower Saxony
- Mining has been an important source of income in Lower Saxony for centuries.
Lower Saxony is also an important supplier of crude oil in the European Union. Mineral products still mined today include iron andlignite . - The
coat of arms shows a whitehorse (Niedersachsenross ) on red ground, which is an old symbol of the Saxon people
- Was originally a duchy
- It is named after the Saxons
- Originally the region was simply called "Saxony", but as the center of gravity of the
Duchy of Saxony gradually moved up the Elbe, towards the present-day states ofSaxony-Anhalt andSaxony , the region was given the name of Lower Saxony - The state was founded in 1946 by the British military administration, who merged the former states of Brunswick, Oldenburg, and Schaumburg-Lippe with the former
Prussia n province of Hanover
http://www.gtp.gr/LocPage.asp?id=14414
http://www.germanfoodguide.com/niedersachsen.htm
http://en.academic.ru/dic.nsf/enwiki/11155
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)